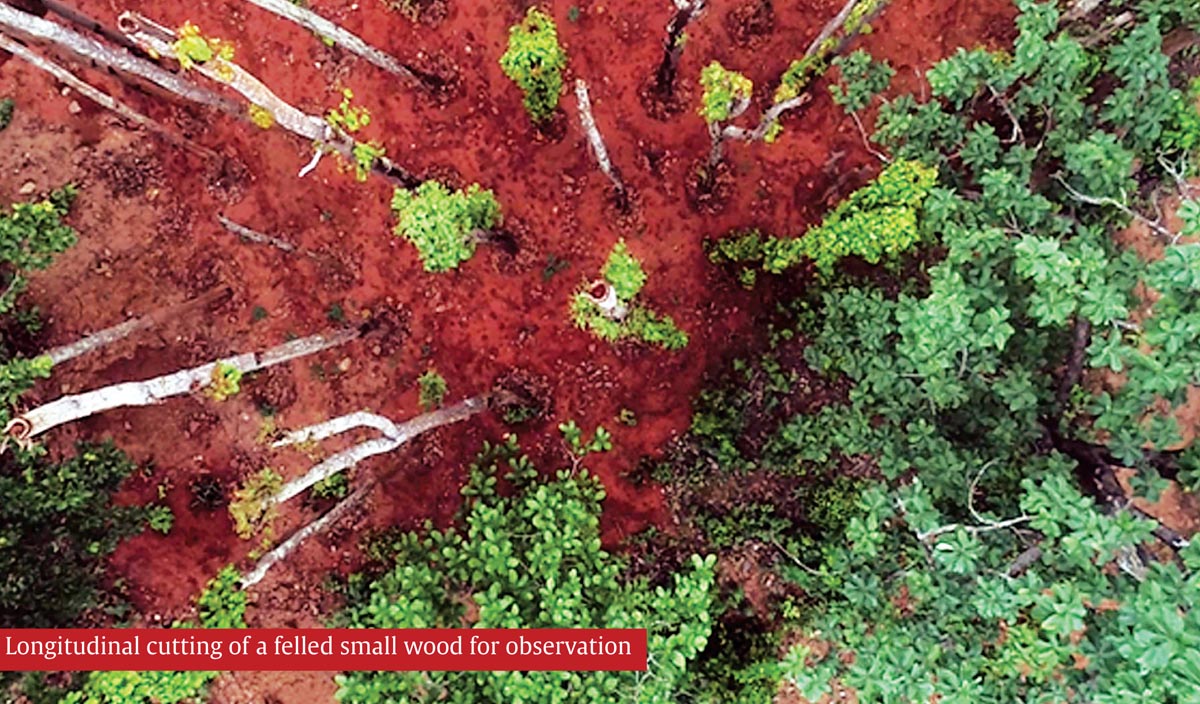
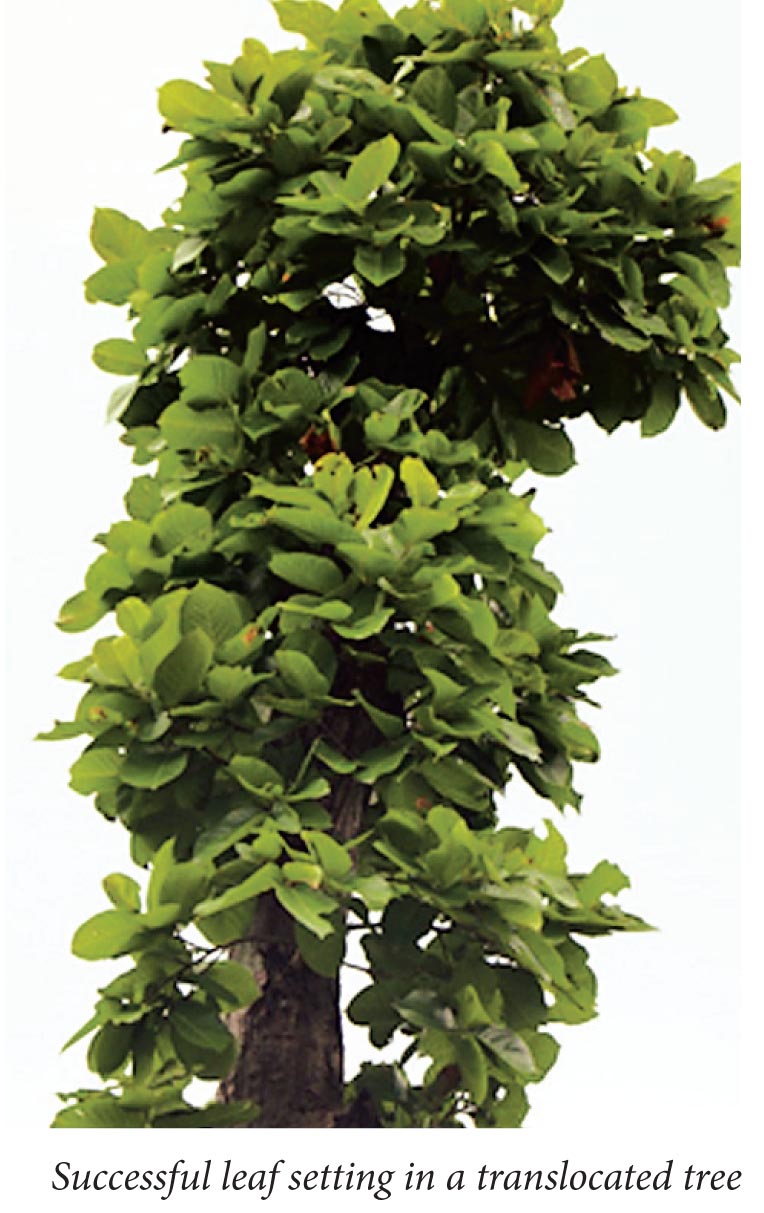
Tree Translocation of 1000 trees in Balliguda Forest Division
By Vishwanath Neelannavar, IFSAs per reports of united nations, total 12,90,000 sqr. km of area of forest is cut down across the world from 1990-2015. This area is 1/3rd of Indian Geographical area. In previous budget of India more than 7.0 Lakh Crore Rupees was earmarked for new road constructions and road widening across India.
This indirectly indicates that, there would be more number of trees will be cut down for the purpose. However, development is also important and priority sector for government. There is always a tussle between development and conservation across the fields.
The Balliguda Forest Division has tried to strike a balance between development and conservation through tree translocation / transplantation. NH circle (South), Berhampur is widening the NH-59 from k.m 173/370 to 229/400 k.m from Balliguda to Daringbadi. The NH authorities had applied for cutting of 2649 number of trees, comprising of valuable and important trees like sal, ficus etc. The joint inspection along with Executive Engineer (NH) division was conducted and it was decided to translocate all feasible and possible trees. The promising and young trees were identified and numbered with GPS locations and it was decided to translocate 1000 trees. The trees were marked and separate list prepared. Total 34 species were chosen for translocation. The trees which are promising and old history of their survival rate were considered. There was no good literature or the articles regarding success rate or the
survival rate available for most of the trees. Therefore, maximum number of trees was selected, which had record of good survival rate.
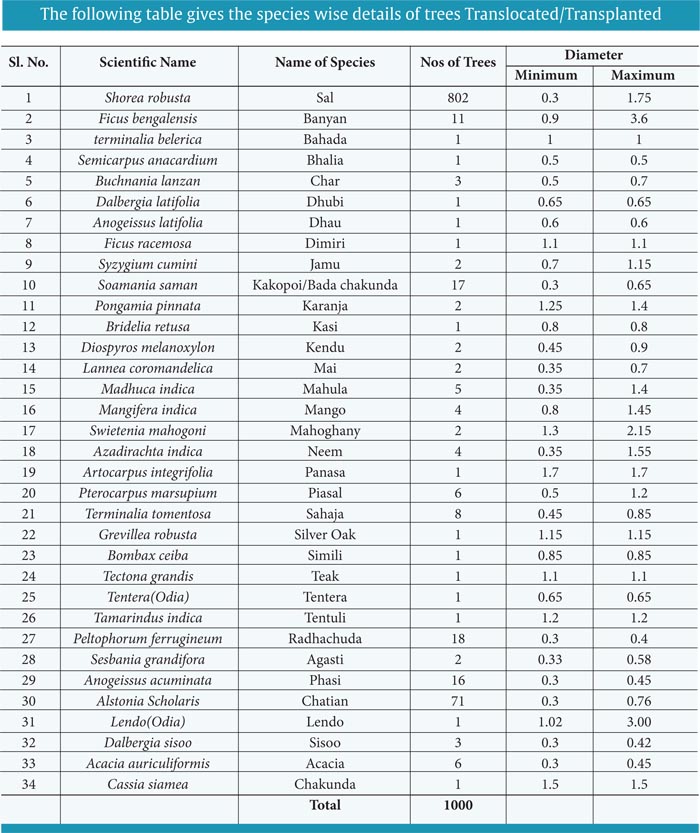
The experiences of Karnataka, Jharkhand, Maharashtra was considered and based on their experience the trees were selected. Also, to experiment the other unknown species, the trees were chosen in very few numbers ie two to three only. The following table gives the species wise list with diameter which was chosen for the translocation.

Methodology for Tree Transplantation adopted
Initial Tree Assessment
- The first and foremost step in tree transplantation is assessing the tree whether it is transplantable or not.
- The selected tree shall be healthy, free from all pests and diseases. The roots shall be properly formed and free from all external damages.
- The tree should be sturdy and should withstand the shock of transplantation.
- The site from where the tree is to be removed and the site where the tree is placed should be approachable and should be free from all underground and overhead utilities Steps in Tree Transplantation
A. Trimming of Branches
Trimming of the tree crown before transplanting shall be done following the below procedure
- Overall shape shall be maintained and structure of tree shall not be destroyed
- Long shoots, diseased or infested branches, overlapping and crossing shoots, and unwanted shoots growing from the trunk less than 2 meters from the ground shall be removed till the base of the stem.
- For broad leaved deciduous trees without prominent trunk, only branch thinning shall be done.
- Wounds shall be smooth without splitting
- Where ever there is a wound, they shall be smoothened with fungicides like Copper Oxy Chloride which is a contact fungicide.
- Trimming of branches shall e done to balance the root shoot ratio and also fit in the available transportation vehicle.
B. Digging of Tree
- The diameter of the excavated root system or soil ball shall be four times the diameter of the base of the tree trunk, but not less than 40 centimeters. The depth of the excavation shall be 2/3 of the soil ball’s diameter, but not shallower than 25 centimeters. The depth of the soil ball shall include multiple root systems
- When encountering thick roots, cut shall be made with a hand saw instead of digging through, keep the wounds smooth and healing agents shall be applied to prevent infection.
- All cuts wherever made shall be clean and sharp without damaging the tissue of plant.
C. Burlaping the Tree
- The soil ball or Root Ball shall be burlaped with suitable materials like Hessian cloth and then with a plastic tape. The Plastic tape shall be supported with Nylon rope.
- The hessian cloth shall be thick enough to hold the soil from not falling after lifting the tree
D. Lifting the Tree and Transporting
- Laoding, Unloading shall be gentle and avoid dragging. Cushionsshall be placed between the body ofvehicle and the tree to prevent any aberrations.
- tree being transported shall beprotected from strong wind, strong sun light, Rain Cold weather and thef
- While transporting, loading and unloading, traffic safety guidelines shall be followed, with warning signserected to alert passing vehicles and pedestrians.

E. Tree Planting:
- Marking the pit shall be done in advance and approvals shall be obtained from the concerned authority before digging the pit
- Size of Excavation shall be double that of soil ball or atleast 30 cms wider than its diameter and hole depth shall be 15-20 cms deeper than the root ball
- After digging the tree shall be erectedin the pit and the pit would be refilled with proper backfill soil.
- The backfill soil shall comprise of 40% red soil, 20% Original Soil, 20% rganic fertilizers, 10% Pumice and 0.1% Root promoting hormones
- There shall not be any rocks or impurities larger than 1 cm in diameter in the soil.
- As far as possible Transplantation process shall be completed on the same day
- Compaction shall be done around the tree while refilling the pit
- Supporting structures would be installed for lean and weak trees n Watering the tree would be done immediately after tree plantation
F. Maintaining the Tree
- Watering of tree shall be done immediately after transplanting, and watering shall be done again after 2 -3days, and then again after one week.
- Maintenance of tree shall be done by timely watering and with adequate quantity of water
- Suitable fertilizers mostly organic shall be used to nurture the tree
- Anti transpirants shall be used when ever required based on the species.
G. Safety Procedures and Care while Transplanting
- Appropriate Personal Protective Equipment (PPE) shall be supplied and maintained for all workers. PPE used shall include a hi-visibility mjacket, safety shoes, and gloves.
All chemicals, pesticides, fungicides will be handled with care and register shall be maintained for how empty containers/ cans/ bottles are disposed Results, Discussion and Learnings from Tree Translocation work
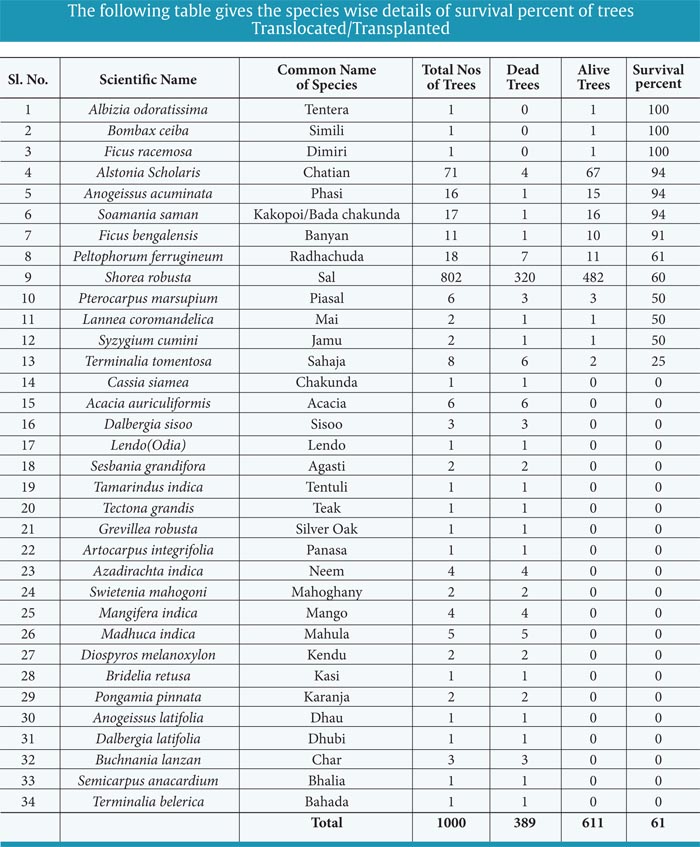
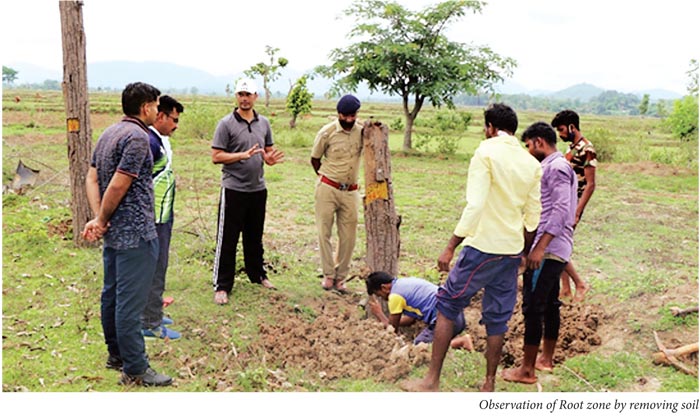
- After completion of second summer and maintenance work, the field verification was conducted on 15th June 2020. Out of 1000 trees, it was expected that about 75-8% trees would survive. However, the casualty observed as per ocular estimation was on a higher side. The reasons for the same were studied in detail during the visit. The team of two ACFs, Forester, and five squads with required equipments, proceeded to the spot verification. The following are the Observation, Learning out of the translocation work.
- It is pertinent to mention here that the COVID-19 had affected the watering and the maintenance work during March and April, 2020, which is most important time for watering. The availability of the labours and the tractor were difficult to find and due to lockdown and fear of corona, no one ventured outside. The field visit of the experts who were at Hyderabad was also restricted leading to the increase in the casualty of the trees in due course of time. It is predicted that, during to COVID-19 lockdown considerable number of trees might have died for lack of watering in peak summer. The analysis was done for the trees which were dried/dead and also the trees which were live. The soil sample was collected as per the procedure and sent for analysis. The stem of the dried tree was cut and studied for insects and pest attack. The following are the details of the field visit.
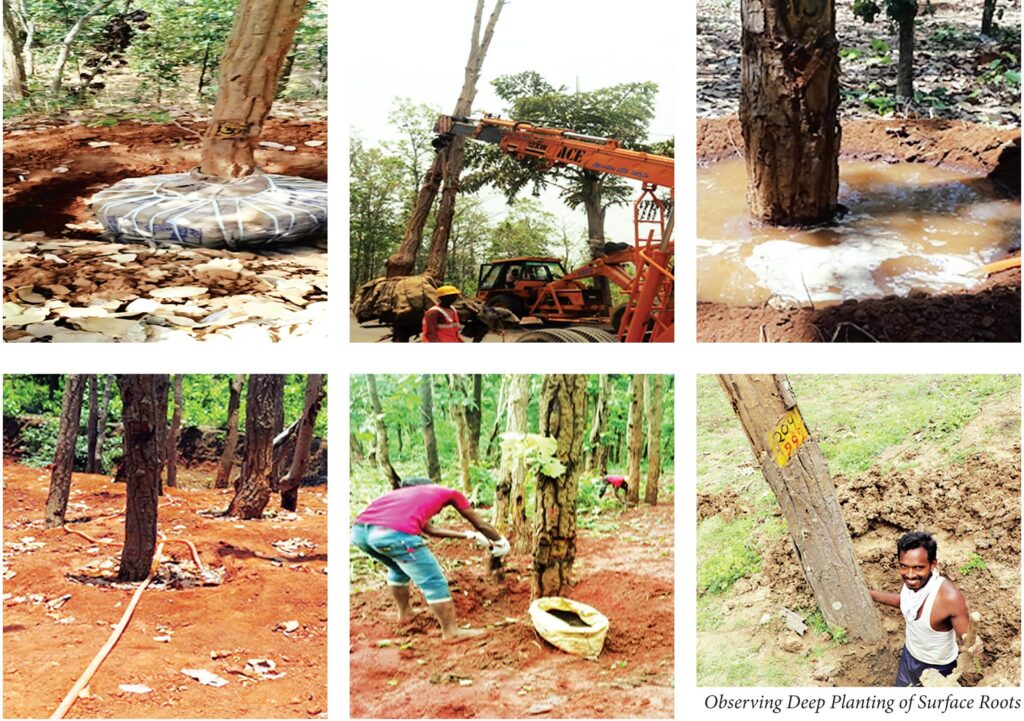
Tree number 204
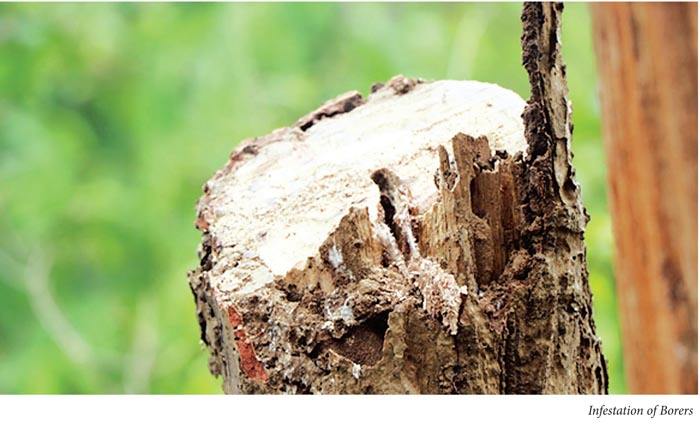
During inspection of the site Tree No.- 204 (Sal) was chosen as it was dead and was just adjacent to the agriculture field. The sprouting was noticed after first rain, however, later on the tree showed wilting symptoms and in due course of time all the leaves dried and eventually the tree died. To find out the reason, the tree stem was observed and there was stem borer attack. The soil was dug to observe the root system, it was found that the root was completely decayed and the depth of the planting was very deep. The soil was very hard and there were hard pans which made the anaerobic condition. The soil sample was collected from the root opening zone
- As per observation and feel method by forming clod, the soil seems to be alkaline with higher content of silt and clay
- The stem of the tree found to be exposed by the action of stripping of barks
- Presence of termites in the root zone and in the stems was rampant
- Presence of insect burrows were plenty which seems to be sal borer and the infestation was quite higher
- After digging for about4 feet, it was observed that
The soil moisture content is very high which had created an anaerobic condition for the root zone - The tree planting is very deep as the roots were still not found after digging for 4 feet
- The water table in that area was very near as capillary water was found in the dug place, the dug place was half filled with water in the second observation after 3 hours
Learnings & Recommendations:
- Tree planting should not be very deep the surface roots should be very close to the ground. In case the tree height is more, the mechanical support shall be provided to avoid the damage due to heavy winds and high rains.
- Selection of the site is very important.The site so selected shall be loamy or sandy loam with better drainage system. The land just adjascent to the paddy fields shall be avoided as it contains hard pans and poor drainage of water.
- Application of VAM amount should be more i.e. 100 g/ tree as it helps to establish the root system
- Site shall have proper surface and sub-surface drainage and proper aeration for the root system todevelop.
- The tap root or the main root shall be cut with axe or other equipments which can give sharp cut. This ensures that there will be least damage to the root and probable damage to the roots could be avoided.
- Soil treatment should be done to reduce acidic or alkaline nature of the soil as per the standard procedure.

Observation for Tree No. 238:
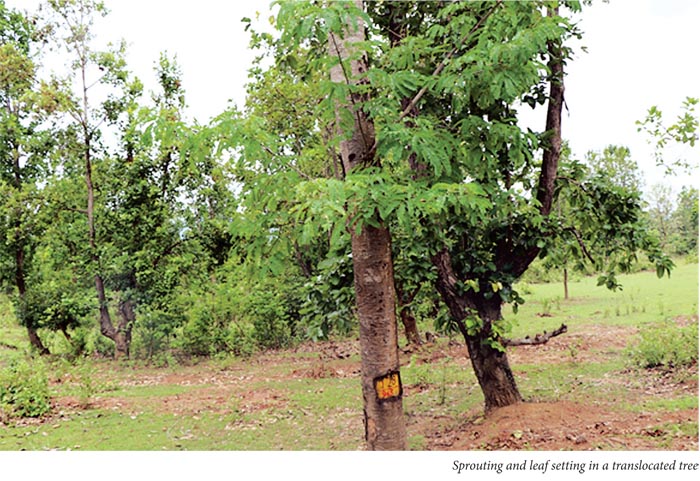
This tree is a Sal tree and is near to the paddy field, however, the distance was little bit away from the field. The soil was good and there was some elevation. This tree had sprouted in the first rain and dried in the subsequent time. However, in the second summer there was sprouting and the tree was live.
Observation for Tree No. 538 and 540:
This tree number 238 is a Ficus tree, and 540 was a tamerind. Both the trees were in dried condition, and the bark and stem were found to be heavily infested by borers and termites with decayed portions.The soil condition was all good with proper drainage, the soil was seemed to be Read loamy soil.
Learning:
The systemic insecticides shall be applied twice in a month for initial period till the stem borers and other insects are under control. The schedule may be prepared for the same for proper follow up.
Observation for Tree groups No. 764/755/783/689:
These trees were observed the were found to be in good establishment condition. The soil condition was observed, the soil was seemed to be Read loamy soil having proper drainage. The survival percentage was good. However there were some trees found dried, and on observation, it was found that the depth of the trees was very deep. Further, this group of trees the top main shoot was cut and there was good sprouting when compared to the group where the top was not cut. This may be attributed to the epical dominancy.
Observation for Tree groups No. 850/851 etc
The tree no 851 was earlier in dry condition, however, in the second season, the trees showed good sprouting and it was having good sprouting.



The presence of Sal Stem borer was present in this transplanted tree. In tree number 850 the observed soil condition and tree condition was good, and it was predicted that the tree would survive. However in the second season the tree showed drying symptoms and it might have died due to deep planting. This tree showed good sprouting in the first season and died in due course of time.
Observation for Tree No. - 610
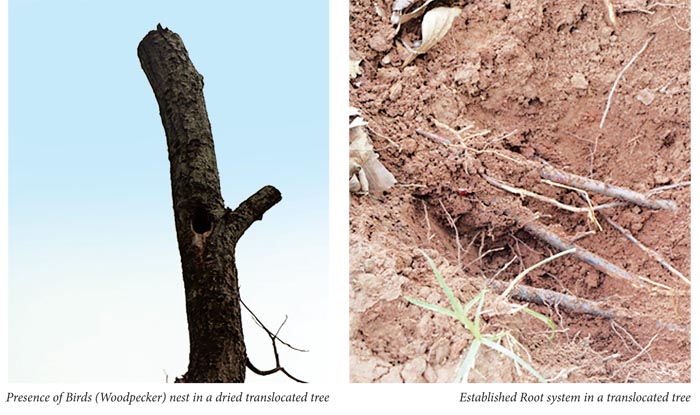
The tree was in live condition in both the years, the root was analysed and the primary and secondary root formation was there. Growth and establishment was found to be good.
Observation near Tree No. - 1847
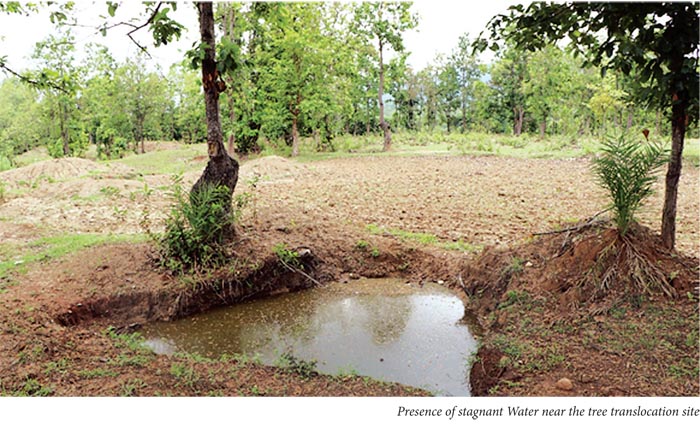
Soil sample was collected near the tree, The top soil up to 1 foot was observed to be moderate clay. After digging for 1 foot a hard pan was observed, It was felt that there was lack of soil aeration near the root zone, a pit of stagnant water was present adjacent to the trees. The digging was very tough due to presence of hard pan.After digging for 2.5 feet root was found, the root was damaged and partially decayed. The planting in the group of trees was found to be very deep. As per information the site was earlier used for rice cultivation. A portion of stem was cut longitudinal and transverse manner, Presence of termites, presence of cavities of sal stem borer and of some other insects were observed.
Observation near Tree No. - 1931
The site was observed, as per information it was earlier a cultivation site, after 6” of digging hard pan in small patches was found. The soil has moderate clay. Partial water logging was found in the site. The planting was found to be very deep. Soil sample was collected and the root was found to be in rotten condition. The soil appeared to be good and had god drainage as there was good slope.

Important Learnings:
- The trees were tilted or bent from one side to the other to break the main root, then the tree is lifted, this caused the considerable damage to the roots. The other alternate like giving sharp cut to root may be considered to avoid the damage to the main root.
- Sufficient time gap may be given after root ball preparation, so that the secondary and tertiary roots are developed inside the root ball. By this method, the root development is ensured and the chances of survival of the tree are more. This way we can ensure better survival rate.
- The percentage of the roots retained in the root-ball was about 5 percentage of the total roots system. The possibility of increasing the root volume may be considered depending upon the species and its root system.
- The soil testing shall be made before shifting the trees and the site should have sufficient drainage and should have good texture and structure.
- There shall be minimum 3 meter gap between the tress for better competition among the trees. The planting of the trees in a group may be encouraged so that the maintenance work like watering and foliar application or soil drenching of the fertilizers is made easy.
- The pitting work shall be done at least 30 days in advance, so that the soil is exposed to the sun for insulation. The application of the vermicompost and other biofertilizers shall be done quite in advance so that the soil quality is improved.
- Planting of the trees shall be shallow; the root-ball shall be placed just one foot below the surface. The mechanical support (may be bamboo or other materials) shall be provided so that three is protected from the winds and other damages.
- The maintenance of the trees shall be at least five years for better survival rate. This will ensure regular watering and use of pesticides or insecticides as and when required. The insecticides and pesticides shall be used on a regular basis based on the infestation.
- The application of the DAP to the trees shall be about 30 cm deep and there shall be watering immediately after the application of the fertilizers. Some of the local residents informed about surface availability of traces of DAP and intake by their cattle, the DAP is toxic to the cattle.
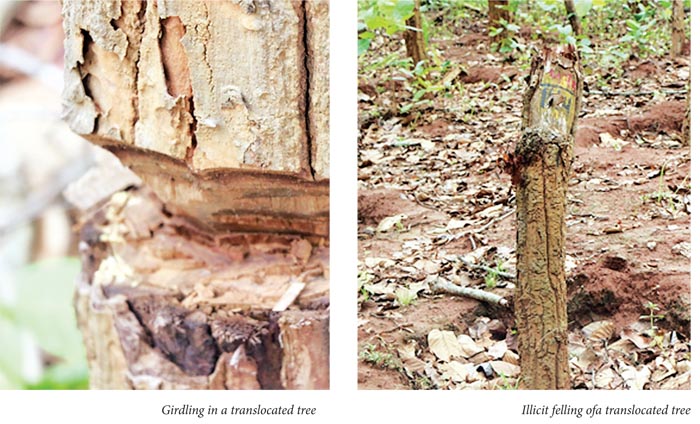
- The patrolling shall be increased as there were some illicit felling of the translocated trees and the girdling of the trees were also noticed. The local staff informed that the UD case has been lodged and the investigation is in progress.







Related Posts
Strangulation by cementing is the silent killer of trees in urban environments
Strangulation by cementing is the silentkiller of trees in urban environments By Sundararaj R, Swetha…
Guardians of Grey Headed
Guardians of Grey Headed Observations by CA. Shomi Gupta & Yogesh More The Grey Headed…
Participation of women in Natural Resource Management
Participation of women in Natural Resource Management By Anubha Srivastav and Anita Tomar Natural Resource…
Vulture – A lost magnificence
Vulture – A lost magnificence By Nitish Agrawal Madhya Pradesh has a rich diversity of…




